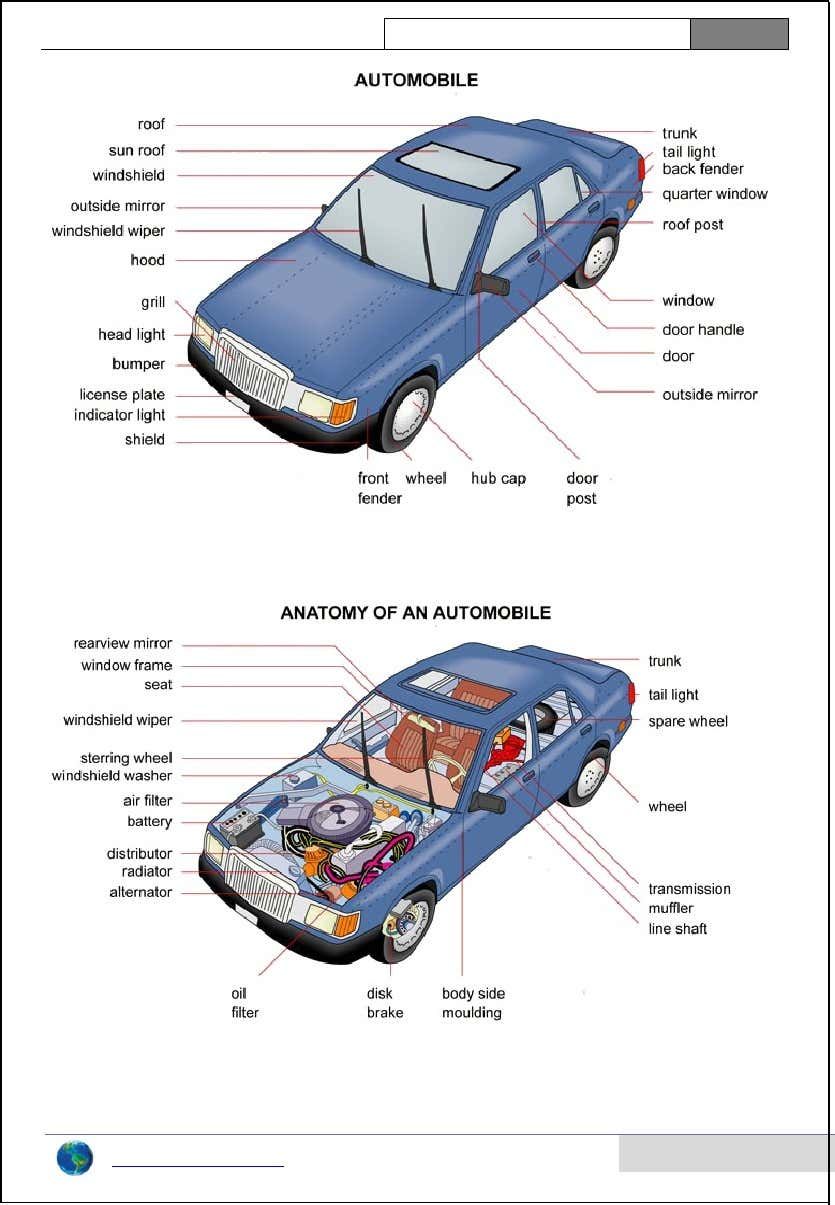
Accurate labeling of car parts is a cornerstone of efficiency, safety, and precision in the automotive industry. Whether in manufacturing, repair, or customization, clear and consistent labeling ensures that components are correctly identified, assembled, installed, and maintained. From a tiny bolt to a complex engine component, each part plays a vital role in a vehicle’s performance, and mislabeling can lead to costly errors, safety hazards, or operational delays.
Types of Labels and Their Applications
The automotive sector employs various labeling techniques tailored to specific needs:
-
- Part Numbers and Codes: Unique identifiers like SKUs or OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) codes allow technicians and suppliers to order, track, and replace parts accurately. For example, a brake caliper with a specific part number ensures the correct replacement is sourced, avoiding compatibility issues.
-
- Diagrams and Annotation: Technical diagrams with labeled parts help workers visualize assembly processes. A detailed engine bay diagram, for instance, can guide a mechanic through replacing multiple components without disassembling the entire engine.
-
- Color-Coded Labels: Systems like red for electrical components, blue for fluids, or yellow for hazardous materials streamline quick identification during repairs. This minimizes trial-and-error, especially in emergency scenarios.
-
- Temporary vs. Permanent Labels: In production lines, removable tags might mark work-in-progress modules, while permanent etching or laser-engraved labels ensure longevity on finalized parts.
Best Practices for Effective Labeling
To maximize clarity and durability, automotive professionals follow key practices:
-
- Durability: Labels must withstand heat, moisture, and chemicals. Waterproof adhesive labels or metal nameplates are common solutions for harsh environments.
-
- Visibility: Labels should be positioned in accessible locations, avoiding cluttered areas. For example, engine components under heavy vibration require labels anchored securely to prevent wear.
-
- Consistency: Standardized labeling systems across teams reduce confusion. A nationwide repair chain, for instance, might adopt a uniform part numbering system to unify its workforce.
-
- Regulatory Compliance: Labels must adhere to industry standards, such as OSHA’s hazard communication guidelines, which mandate clear warnings for toxic substances or flammable materials.
Technologies Enhancing Labeling Precision
Advances in technology have revolutionized automotive labeling. Laser engraving machines inscribe part numbers directly onto metal surfaces, resisting wear and tampering. Printing technologies like inkjet printers produce high-resolution labels on-demand, reducing inventory costs. Meanwhile, RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) tags embedded in components enable automated tracking throughout a vehicle’s lifecycle—from assembly to recycling. QR codes linked to digital part databases further facilitate instant access to specifications via smartphones, bridging physical and digital workflows.
Impact on Operational Efficiency
In manufacturing, labeled components accelerate assembly lines by reducing misplacement and rework. At repair centers, precise labels minimize diagnostic time, allowing mechanics to focus on repairs rather than deciphering part identities. For consumers, clear labeling on aftermarket parts boosts confidence in DIY installations, reducing returns and warranty claims.
Accurate part labeling is more than a logistical task—it’s a critical safety and efficiency driver in the automotive industry. By leveraging standardized systems, durable materials, and cutting-edge technologies, manufacturers and technicians ensure that every component, from the smallest screw to the largest engine block, contributes reliably to vehicle performance. As automotive technology evolves, innovations in labeling will remain essential to keeping pace with the complexity of modern vehicles.




